optic nerve thickness test|normal optic nerve sheath diameter : company Nerve Fiber Analyzer (GDx): GDx uses laser light to measure the thickness of the nerve fiber layer. There are nuances between the instruments, but they all serve the purpose .
1 de mar. de 2023 · -Novas Atualizações linha tocom. -Sobre estas versões:-Correção automática do auto PID.-Ajustes na segurança do sistema.-Ajustes gerais de bugs. .
{plog:ftitle_list}
WEB461K Followers, 656 Following, 124 Posts - See Instagram photos and videos from GABRIELY MIRANDA (@gabrielymiiranda)
As a stand-alone test, RNFL analysis has great diagnostic ability to detect early glaucoma. 5,6 Most OCT platforms provide RNFL thickness values at a fixed distance away from the optic .The Stratus OCT measured retinal nerve fiber layer (RNFL) thickness via a 3.5-mm-diameter circle centered on the optic disc and used radial scans to provide measurements of the optic nerve head (ONH) such as disc, cup, and rim area. The OCT test can also help doctors detect changes in the eye, caused by diabetes and macular degeneration. The test can help doctors quantify abnormal thickening of the center of the retina, known as macular edema, or .The double hump is a graphic plot of the RNFL thickness around the optic nerve that is observed in most normal individuals, with the superior and inferior poles having the greatest RNFL .
This article summarizes some of the tests that you may experience during an eye exam for glaucoma, including the visual field test, corneal thickness and angle tests, optic . Nerve Fiber Analyzer (GDx): GDx uses laser light to measure the thickness of the nerve fiber layer. There are nuances between the instruments, but they all serve the purpose .The Heidelberg Retina Tomograph (HRT) is a special laser that produces a three-dimensional high-resolution image of the optic nerve. This test provides clinicians with measurements of . Retinal nerve fiber layer thickness represents the ganglion cell axons before they enter the optic nerve. Loss of retinal nerve fiber layer can be observed in red-free photos and is quantified with OCT. The peripapillary .
Optical coherence tomography (OCT) and optical coherence tomography angiography (OCTA) are non-invasive imaging tests. They use light waves to take cross-section pictures of your retina. With OCT, your . The optic nerve is part of the eye, the central nervous system (CNS), and one of the 12 cranial nerve pairs. 1 It’s also known as the second cranial nerve or cranial nerve II. The optic nerve is responsible for . An optical coherence tomography test is a quick and easy imaging test that can help your provider see to the back of your eyeball. It provides three-dimensional images of the different layers in your eye. This helps them take measurements and examine your optic nerve for potential damage.
BACKGROUND AND PURPOSE: No MR imaging measurement criteria are available for the diagnosis of optic nerve atrophy. We determined a threshold optic nerve area on MR imaging that predicts a clinical diagnosis of optic nerve atrophy and assessed the relationship between optic nerve area and retinal nerve fiber layer thickness measured by . Optic disc (coronal view) The optic nerve head (also known as the optic disc) is approximately 1.5 mm wide and is also associated with a physiological cup that corresponds to a central depression in the optic nerve head.The dimensions of the cup and disc are dependent on the orientation, shape and size of the chorioscleral canal that exists at Bruch’s membrane. Visual acuity test. Visual acuity testing assesses multiple modalities of eye function. It gives an idea of the optical integrity of the eyes, as well as the health of the retina and the ability of the brain to interpret the images. The test is often performed in a well-lit environment, with the patient standing or seated at least 6 meters away from the Snellen chart (a placard .
Artificial Increase in Retinal Nerve Fiber Layer Thickness. Gliosis of the optic nerve and retinal axons following optic nerve damage can result in an increase in RNFL thickness despite significant atrophy of axons. . map in the perifoveal location should be scrutinized carefully and correlated with the clinical exam and functional tests. It . This test measures the thickness of the eye's retinal nerve fiber layer, which is often thinner from optic neuritis. Visual field test. This test measures the peripheral vision of each eye to determine if there is any vision loss. Optic neuritis can cause any pattern of visual field loss. Visual evoked response. Two common imaging tests include a simple high-resolution color photograph with a very bright flash from a professional camera, and a quick laser scan of the optic nerve. Scans can detect small nerve fiber layer changes of the optic nerve at the micron level. It can help measure the thickness of the nerve fibers and detect any abnormalities. – Fundus photography: This test involves taking photographs of the back of the eye, including the optic disc. . An optic nerve damage test is a diagnostic test used to evaluate the health of the optic nerve and detect any damage or abnormalities. This may .
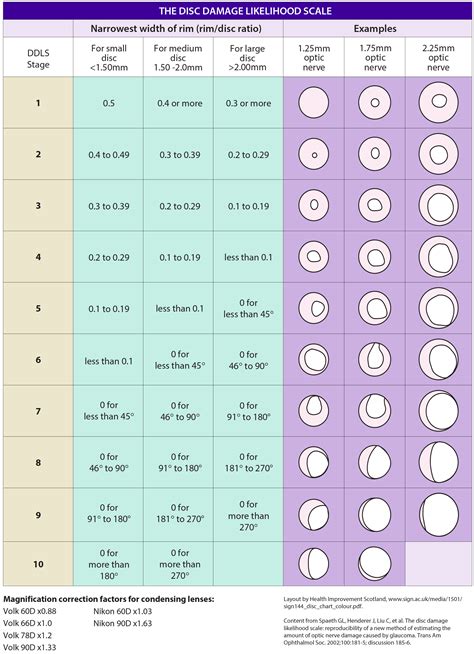
optic nerve size chart
RNFL thickness is greatest at the optic nerve head and decreases as the distance away from the nerve increases. 20-22 While mild shifts in scan position do not significantly alter RNFL measurements, moderate to severe misalignment can cause a shift in the TSNIT curve, resulting in artificial thinning or elevation. 20 Truncation artifacts result . Optic nerve coloboma: This is an inherited condition that affects and disrupts optic nerve development. It can happen to one or both eyes. Optic nerve drusen: These are deposits made of protein, calcium and fatty compounds. They can build up in various places near the backs of your eyes, including your optic nerve. Non-invasive, non-contact optical coherence tomography (OCT) provides real-time, cross-sectional images of the retina and measures the thickness of the Retinal Nerve Fiber Layer (RNFL) Thickness. This test can be used to diagnose and help to manage several retinal and optic nerve diseases. 1. Background. Glaucoma is an asymptomatic ocular disease characterized by a progressive loss of retinal nerve fibres and increased cupping of the optic disc due to several cellular disease phenomena in the eye [].Glaucoma, particularly primary open-angle glaucoma (POAG), is the leading cause of irreversible blindness in the world [2, 3].Global projections .
Optic nerve OCT. Optic nerve and nerve fiber layer OCT helps in the management of glaucoma. The OCT machines provide automated, serial analysis of the nerve fiber layer thickness, cup-to-disc ratio, and other measurements. .
Ophthalmoscopy (examination of the back of the eye): Examination of the shape and color of the optic nerve, also called a dilated eye exam; . Pachymetry is a simple, painless test that measures the thickness of the cornea—the clear .
The RTVue device scans the optic nerve head with multiple radial and circular scans and generates the RNFL thickness map along a 3.45-mm diameter circle centered on the optic disc. Each of the OCT devices provides .Purpose: To determine the effects of age, sex, and race on the retinal nerve fiber layer (RNFL) in the normal human eye as measured by the spectral domain optical coherence tomography (SD-OCT) Spectralis machine (Heidelberg Engineering). Methods: Peripapillary SD-OCT RNFL thickness measurements were determined in normal subjects seen at a university-based clinic.
OCT retinal nerve fiber layer imaging technology has had an amazing impact on our ability to diagnose glaucoma at earlier stages of the disease. On the flip side, there comes a time at the moderate-to-advanced stages of disease when the RNFL analysis at the optic nerve head becomes of limited to no value in monitoring a patient for progression.Keywords: optic disc oedema, optic neuropathy, papilloedema, retinal nerve fibre layer thickness, RNFL thickness. Introduction. Optic disc oedema (ODE) can be a vital manifestation of varied ocular as well as systemic disorders. 1 Some of them are relatively benign, while others may have devastating visual and neurological consequences. ODE is .
Scans with higher signal strengths have less variability, especially when the optic nerve is relatively healthy. Conclusions. . producing a total of 3 separate scans during each test. It generates RNFL thickness measurement for each of twelve 30-degree sectors, then computes an average for each of four quadrants and an overall average.
A test was considered statistically significant at a cutoff level of P<0.05. Bonferroni’s method was used to adjust the significance level for performing multiple statistical comparisons. . Reproducibility of nerve fiber thickness, macular thickness, and optic nerve head measurements using StratusOCT. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2004; 45: .
Most children older than eight years can perform a fairly reliable visual field test. Referral In any case where the diagnosis of pseudopapilledema is not confirmed, referral to a neuro-ophthalmologist is warranted. . 19. Savini G, Bellusci C, Carbonelli M, et al. Detection and quantification of retinal nerve fiber layer thickness in optic . We next measured the effect of optic nerve injury on the structure of the outer retina. The width of the outer retina decreases after photoreceptor damage caused by mutation, light damage, aging and toxin administration [28, 32,33,34].Reduced outer nuclear layer thickness is highly correlated with photoreceptor degeneration and decreased photoreceptor . Made of nerve cells, the optic nerve is located in the back of the eye. Also known as the second cranial nerve or cranial nerve II, it is the second of several pairs of cranial nerves.It is a bundle of nerve cells that transmits sensory information for vision in the form of electrical impulses from the eye to the brain.
Consider these tests during both baseline and follow-up examinations for comprehensive monitoring. Note the enlarged blind spot on automated 24-2 visual field seen in the left eye of a patient. . Staying close to the margin of the optic nerve head on the temporal side, . One study found that the mean peripapillary RNFL thickness in children .Referring to the above link, OCT is a newer test within the past several years which can measure the thickness of the Retinal Nerve Fiber Layers (RNFL) composing the optic nerve. In this test, a laser light is used to scan the internal structures of retina, and in the case of glaucoma, early changes to the nerve fiber layer thickness can be .

wood floor moisture meter lowes

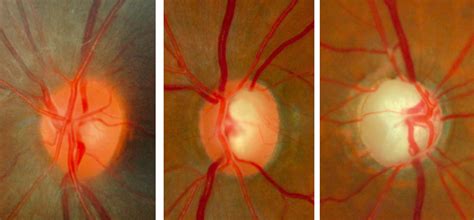
optic nerve different sizes
WEBMalhação: Viva a Diferença conta a história de cinco meninas se conhecem em uma situação inusitada. No elenco, temos Bruno Gadiol, Matheus Abreu, Juan Paiva, .
optic nerve thickness test|normal optic nerve sheath diameter